
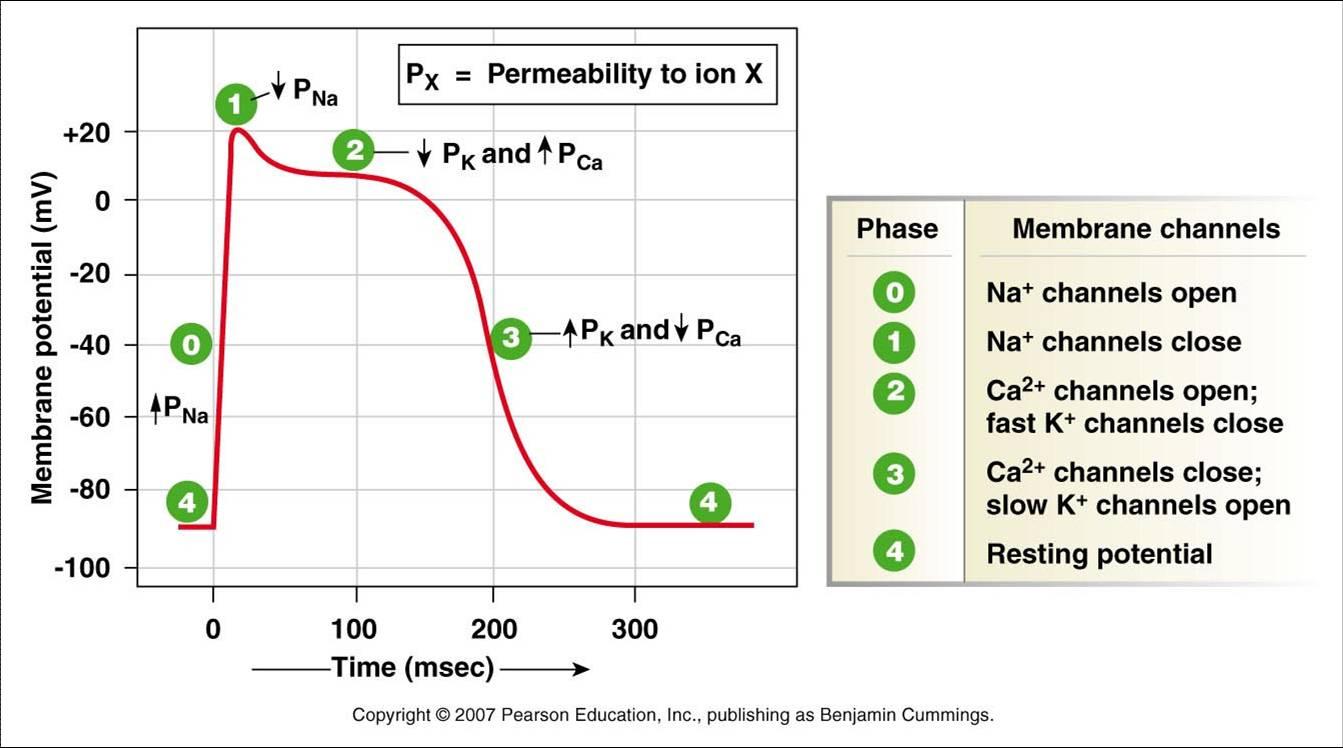
This depolarizes the membrane and brings the potential closer to the equilibrium potential of Na+ (~ +50mV).Īn increase in ionic conductance in the membrane of the axon results in an increase in the action potential. However, during an action potential, the permeability to Na+ is dramatically increased by the opening of Na+ channels. At rest, the membrane is most permeable to K+ thus, the resting potential is closest to the equilibrium potential of K+ (~ -110mV).
This creates a driving force for K+ to go out of the cell and Na+ to come into the cell. is higher inside the neuron while is higher outside the neuron. Membrane potential is determined by the equilibrium potential and relative permeabilities of the ions in the system. In the neuron, the major ions in play are potassium (K+) and sodium (Na+). This difference arises from the separation of electric charges across the resistive membrane barrier. Action potentials enable nerve cells to carry signals over long distances.Īction Potentials are Initiated by a Change in Membrane PotentialĪ neuron at rest maintains an electrical potential difference across its membrane. Action potentials are self-regenerating and occur spontaneously when the membrane is depolarized to a critical voltage called the threshold. It is a brief, explosive change in membrane potential which goes from a negative to a positive potential.
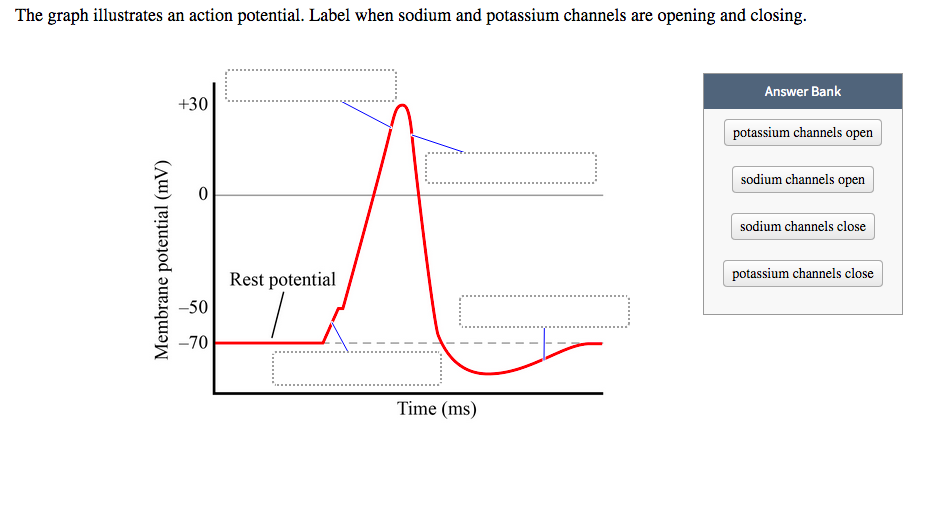
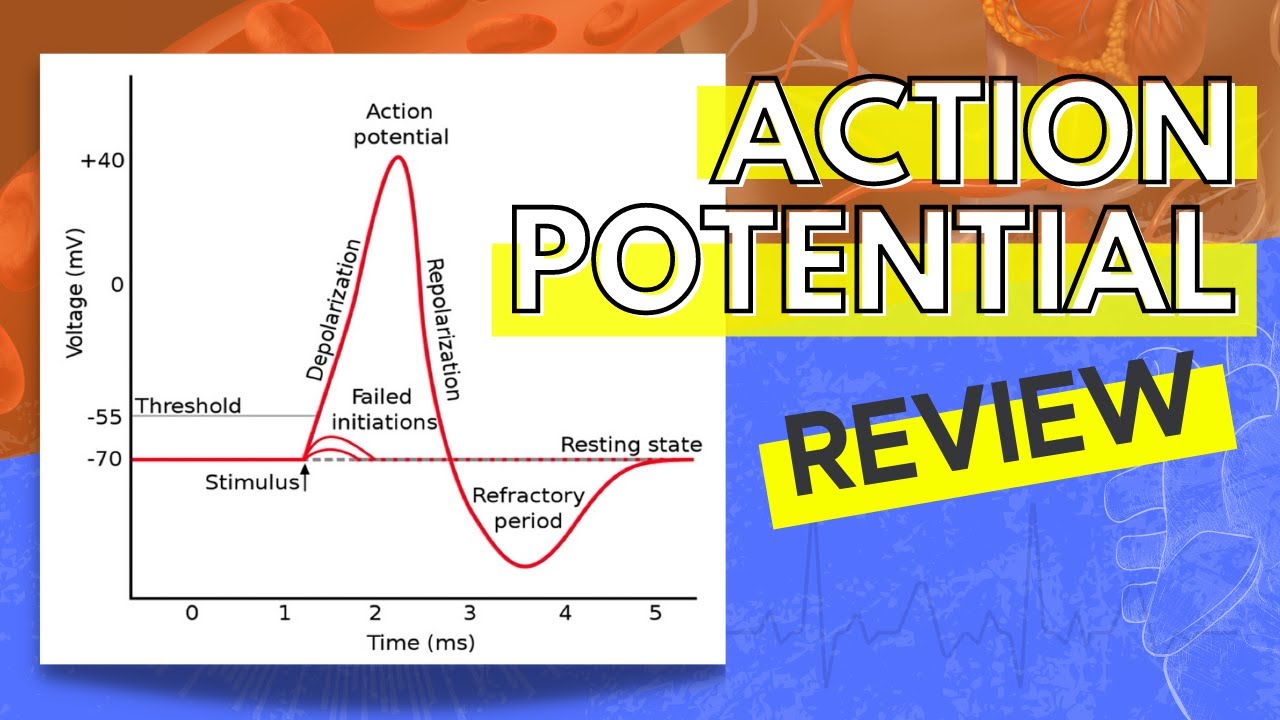
And this is due to sodium channels opening and allowing sodium into the cell. And this is the red line here, so you can see it goes from the resting potential up to about positive 40 mil a bolt. Now the first step of the action potential is going to be deep polarization. Also want to point out the resting potential is slightly below negative 60 and the threshold potential is going to be slightly above negative. We have time in milliseconds and again ranging from about 0 to 4. So this is the membrane potential, ranging from about negative 82 positive 40 on the x axis. So 1/2 a graph here on the X axis we have millet volts. Six from Chapter 46 is looking at what occurs during an action potential.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
